Exploring Four Foundational Concepts in Artificial Intelligence
Exploring Four Foundational Concepts in Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a transformative force, reshaping industries, powering innovations, and redefining the boundaries of human-machine interaction. At its core, AI encompasses a diverse array of concepts and techniques aimed at enabling machines to mimic human intelligence and perform tasks that traditionally require human cognitive abilities. In this blog, we delve into four fundamental concepts that underpin the field of AI: Machine Learning, Neural Networks, Natural Language Processing (NLP), and Computer Vision.
1. MACHINE LEARNING
Machine Learning serves as the cornerstone of modern AI systems. It is a subset of AI that endows machines with the ability to learn from data and improve their performance over time without explicit programming. At the heart of machine learning lie algorithms that identify patterns and extract meaningful insights from vast datasets. Supervised learning algorithms learn from labeled data, mapping input to output, while unsupervised learning algorithms uncover hidden structures within unlabeled data. Reinforcement learning algorithms, inspired by behavioral psychology, learn through trial and error, maximizing rewards to achieve specified goals.
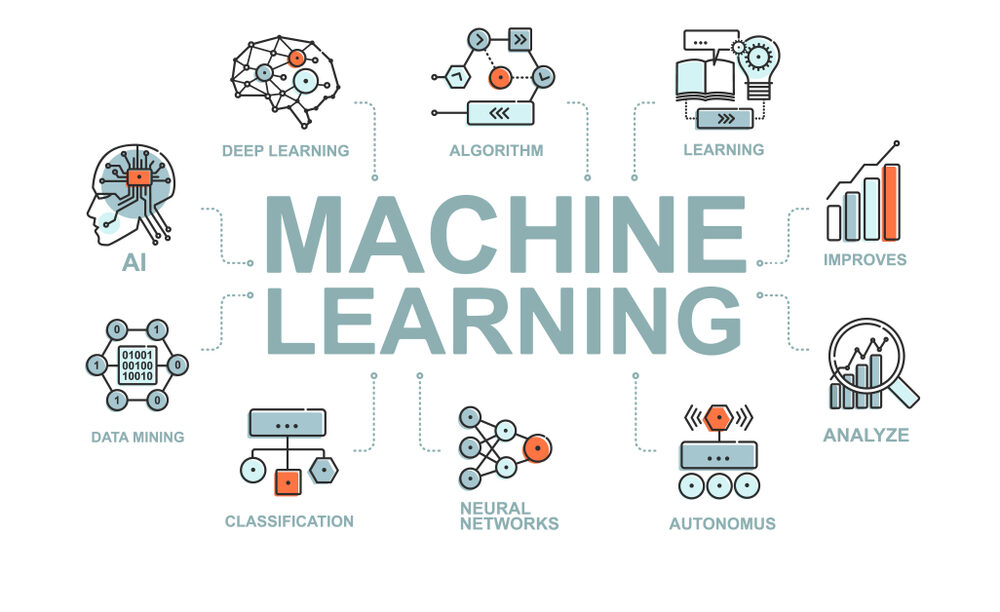
2. NEURAL NETWORKS
Neural Networks, inspired by the structure and function of the human brain, have revolutionized machine learning. These interconnected networks of artificial neurons, organized in layers, excel at tasks such as image recognition, natural language understanding, and pattern recognition. Deep learning, a subset of neural networks, leverages multiple layers of abstraction to automatically extract hierarchical features from data. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are particularly effective in computer vision tasks, while Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) excel in sequential data processing, making them invaluable in NLP applications.

3
3. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural Language Processing (NLP) empowers machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language. From sentiment analysis to language translation, NLP algorithms enable computers to comprehend the nuances of human communication. NLP encompasses various techniques, including syntactic analysis, semantic understanding, and sentiment classification. Transformer models, such as BERT and GPT, have achieved remarkable success in NLP tasks by leveraging attention mechanisms to capture contextual information and generate coherent responses.
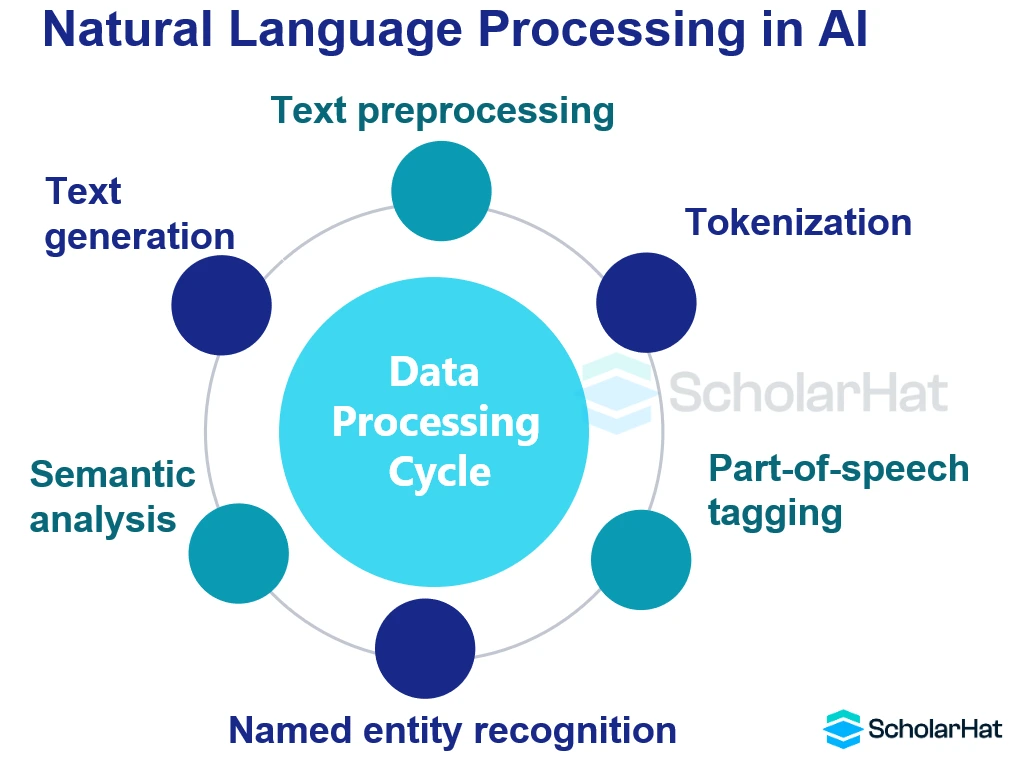
4. Computer Vision
Computer Vision enables machines to interpret and make sense of the visual world. Through techniques like image classification, object detection, and image segmentation, computer vision algorithms can analyze and understand digital images and videos. Deep learning approaches, particularly CNNs, have significantly advanced computer vision capabilities, enabling applications ranging from autonomous vehicles to medical imaging diagnostics. By extracting features and patterns from visual data, computer vision systems can perceive and interpret their surroundings, paving the way for intelligent automation and augmented reality experiences.

In conclusion, the concepts of Machine Learning, Neural Networks, Natural Language Processing, and Computer Vision constitute the foundational pillars of artificial intelligence. Together, they empower machines to learn, reason, and interact with the world in ways previously thought possible only by humans. As AI continues to evolve, these concepts will remain crucial in driving innovation, solving complex problems, and shaping the future of technology and society.
Compiled by: Pratiksha Bisht
Comments
Post a Comment